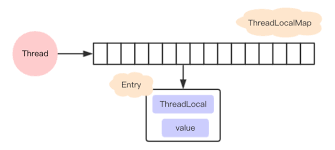
JAVA中ThreadLocal是如何保证线程安全的
1.线程安全
当多个线程试图同时对一个共享变量进行访问修改的时候,容易引发数据不安全的操作。
例如一个线程1正准备对变量进行修改+1时,另一个线程2也进行了修改+1,那么这个线程1进行修改的操作就可能是不成功的。
2.可以采取的措施
3.ThreadLocal使用
ThreadLocal<String> mStringThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
ThreadLocal是除了加锁之外另外一种保证多线程访问共享变量的线程安全方法,即每个线程对共享变量的访问都是基于线程自己的变量的,也就是说共享变量也还是只有一个,但是每个线程都有一个共享变量的独立拷贝,每个线程只访问修改自己独立拷贝的变量
set方法
mStringThreadLocal.set("string")
get方法
mStringThreadLocal.get()
ThreadLocal初始值
可以通过覆写initialValue来设置初始值
ThreadLocal<String> mThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<String>(){
@Override
protected T initialValue() {
return "init";
}
};
4.ThreadLocal原理
ThreadLocal的set方法,含义:
- 首先获取当前线程
- 获取当前线程的threadLocals,这是一个ThreadLocalMap对象
- 然后判断threadLocals是否为空,如果为空,则把创建一个并赋值,如果不为空,就设置值
ThreadLocal.set方法源码
/**
* Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable
* to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to
* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}
* method to set the values of thread-locals.
*
* @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of
* this thread-local.
*/
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
ThreadLocal.get方法源码
获取当前线程
获取该线程的ThreadLocalMap
然后以this->ThreadLocal为key,在该线程ThreadLocalMap找到相应的值
public T get() { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) { ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); if (e != null) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") T result = (T)e.value; return result; } } return setInitialValue(); }上述中的ThreadLocalMap实际上是Thread对象的threadLocals变量,每个线程都有一个自己的ThreadLocalMap变量
class Thread implements Runnable { /* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained * by the ThreadLocal class. */ ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null; }对应ThreadLocalMap源码
可以看到初始化方法,其中的table是自己独有的那一份,key是ThreadLocal对象
static class ThreadLocalMap { private Entry[] table; ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) { table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY]; int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1); table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue); size = 1; setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY); } private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) { int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1); Entry e = table[i]; if (e != null && e.get() == key) return e; else return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e); } }
总结:可以看到源码中,每个线程调用ThreadLocal.set()方法时,实际上是找自己线程的ThreadLocalMap对象,然后往自己ThreadLocalMap根据key为ThreadLocal,计算hash值,往table里放入东西;每个线程调用ThreadLocal.get()方法,也是先找自己线程的ThreadLocalMap,然后根据ThreadLocal为key计算hash值,找到table数组对应索引位置的value。
5. 会导致内存泄露么
有网上讨论说ThreadLocal会导致内存泄露,原因如下:
- 首先ThreadLocal实例作被线程的ThreadLocalMap实例持有,作为key计算hash值使用,也可以看成被线程持有。
- 如果应用使用了线程池,那么之前的线程实例处理完之后出于复用的目的依然存活
- 所以,ThreadLocal设定的值被持有,导致内存泄露。
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
详细描述:ThreadLocal变量被垃圾回收时,每个线程自己的ThreadLocalMap放入的东西,也就是往ThreadLocal的静态内部类ThreadLocalMap中放入的Entry,ThreadLocalMap中存放的Entry是这样一个结构,key为声明ThreadLocal变量的实例对象,而Value为该线程放入的值,由于这里的key是threadLocal变量的弱引用,当ThreadLocal变量被垃圾回收时其堆被回收,但是静态内部类是属于类对象的,由于key是ThreadLocal变量的弱引用,那么就会出现ThreadLocalMap就会出现key为null,value存在的现象,那么这个value就会出现内存泄漏,无法被GC回收。
其实不用担心查看ThreadLocal中的静态内部类ThreadLocalMap中可以发现其每次调用set、get方法时,会调用cleanSomeSlots方法将本次run中所有key为null的entry清理掉
/**
* Heuristically scan some cells looking for stale entries.
* This is invoked when either a new element is added, or
* another stale one has been expunged. It performs a
* logarithmic number of scans, as a balance between no
* scanning (fast but retains garbage) and a number of scans
* proportional to number of elements, that would find all
* garbage but would cause some insertions to take O(n) time.
*
* @param i a position known NOT to hold a stale entry. The
* scan starts at the element after i.
*
* @param n scan control: {@code log2(n)} cells are scanned,
* unless a stale entry is found, in which case
* {@code log2(table.length)-1} additional cells are scanned.
* When called from insertions, this parameter is the number
* of elements, but when from replaceStaleEntry, it is the
* table length. (Note: all this could be changed to be either
* more or less aggressive by weighting n instead of just
* using straight log n. But this version is simple, fast, and
* seems to work well.)
*
* @return true if any stale entries have been removed.
*/
private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {
boolean removed = false;
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
do {
i = nextIndex(i, len);
Entry e = tab[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == null) {
n = len;
removed = true;
i = expungeStaleEntry(i);
}
} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0);
return removed;
}
本作品采用 知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议 (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) 进行许可。